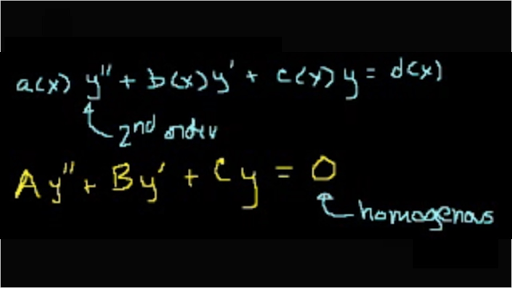Second Order Linear Differential Equation With Variable Coefficients Examples Pdf
Since a homogeneous equation is easier to solve compares to its. Example a A second order linear homogeneous constant coefficients equation is y00 5y0 6 0.

Second Order Linear Differential Equation With Variable Coefficient Youtube
Consider the second order homogeneous linear differential equa-tion.
Second order linear differential equation with variable coefficients examples pdf. Suppose we have a homogeneous linear differential equation of order n with variable coefficients f O 1 and its associated initial conditions given by A0 A k 012 n-l. OF SECOND ORDER LINEAR ODEs HOW TO USE POWER SERIES TO SOLVE SECOND ORDER ODEs WITH VARIABLE COEFFICIENTS. 2 Let y 1 x and y 2 x be any two solutions of the homogeneous equa-tion then any linear combination of them ie c 1 y 1.
That particular integral of. For the equation to be of second order a. A linear homogeneous second order equation with variable coefficients can be written as.
Etc occur in first degree and are not multiplied together is called a Linear Differential Equation. Partial differential equations are used to mathematically formulate and thus aid the solution of physical and other problems involving functions of several variables such as the. Y bxy cxy 0.
Second Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations with Variable Coefficients. Second order linear differential equations. W_ y_1 y_2left x right left begin array 20 c y_1left x right y_2left x right y_1left x right y_2left x right end array right.
T ò V ò T. This is the form of a second-order ODE with variable coefficients. Y a1xy a2xy 0 where a1x and a2x are continuous functions on the interval ab.
Used for second- and higher-order nonlinear PDEs to denote a particular solution see also Preliminary remarks at Second-Order Partial Differential Equations. Second Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients For the most part we will only learn how to solve second order linear equation with constant coefficients that is when pt and qt are constants. The Wronskian of the system of two functions is calculated by the formula.
Differential Equation Order First-Order 2 6 40 Second-Order 3 2 2 𝑖 0 Third-Order 3 3 3 4 Linear vs. Equations with polynomial coefficients are considered and explicit solutions for equations with linear coefficients are given showing significant differences in the functional form of solutions of differential equations from those of difference equations. Solve N 6 T.
C A second order linear non-homogeneous variable coefficients equation is y00 2t y0 lnt y e3t. Y_1left x right cos x y 1 x cos x y_2left x right sin x. So naturally an equation of.
B A second order order linear constant coefficients non-homogeneous equation is y00 3y0 y 1. Optional topic Classification of Second Order Linear PDEs Consider the generic form of a second order linear partial differential equation in 2 variables with constant coefficients. If possible I would wish to avoid obtaining the solution as an infinite.
D2y dx2 6 dy dx 8y 0 Write down the general solution of this equation. The auxiliary characteristics equations for this differential equations is or Implies. 112 Linear Differential Equations LDE with Constant Coefficients.
If Implies by using the method of linear second order differential equation with constant coefficients 17-18. We see that the second order linear ordinary differential equation has two arbitrary constants in its general solution. Second Order Linear Differential Equations Homogeneous Non Homogenous v p q g are given continuous functions on the open interval I c 0 g t y p t.
For finding the solutions of linear second order differential equations. Non-constant function cx or both one or both coefficients of coursevary they become variable. The given equation can be written as ò 2 V ò T 2 6 T 1 Integrating 1 w.
Equations of first and second order. We consider the homogeneous equation. D2Cdeta2 2eta1etadCdeta- keta2C0.
Linear Differential Equations of Second and Higher Order 111 Introduction A differential equation of the form 0 in which the dependent variable and its derivatives viz. Y 2 x sin x. Y px y qx y 0 where px and qx are continuous functions then 1 Two linearly independent solutions of the equation can always be found.
A differential equation is called linear if it. The most general linear partial differ ential equation of order two in two independent variables x and y with variable coefficients is of the form 4 N 5 O 6 P 2 L 3 M V 2 w here 4 5 6 2 3 are functions of T and U only and not all 4 5 6 are zero. Recall the general second order linear differential operator Ly yO pxy qxy 1 where pq 0 CI I ab.
Linear Independence of Functions. When bis replaced by anon-constant function bx or cis replacedby a. The functions y 1x and y 2x are linearly independent if one is not a multiple of the other.
Example 5 Verify that y 1 e4x and y 2 e2x both satisfy the constant coefficient linear homogeneous equation. 2 Let Kt T be the solving kernel of the homogeneous equation ie. A u xx b u xy c u yy d u x e u y f u gxy.
Y by cy 0 where the coefficients band careconstants.

10 Cf Pi Problem 1 Differential Equations Of Higher Order Youtube
Integration And Differential Equations
Ordinary Differential Equations
What Is The Suitable Method To Solve This Nonlinear Partial Differential Equation
Ordinary Differential Equations
Integration And Differential Equations

2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1 Video Khan Academy

Reduction Of Order Linear Second Order Homogeneous Differential Equations Part 1 Youtube
Integration And Differential Equations
2nd Order Linear Homogeneous Differential Equations 1 Video Khan Academy
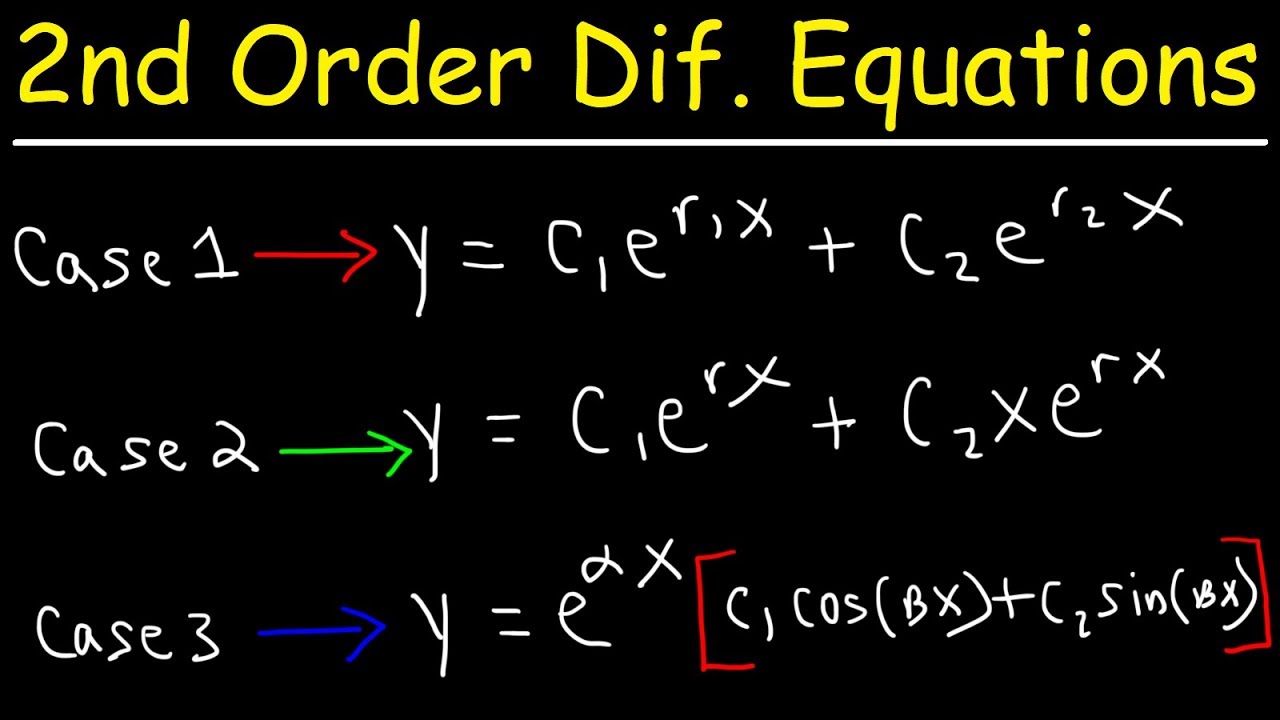
Second Order Linear Differential Equations Youtube
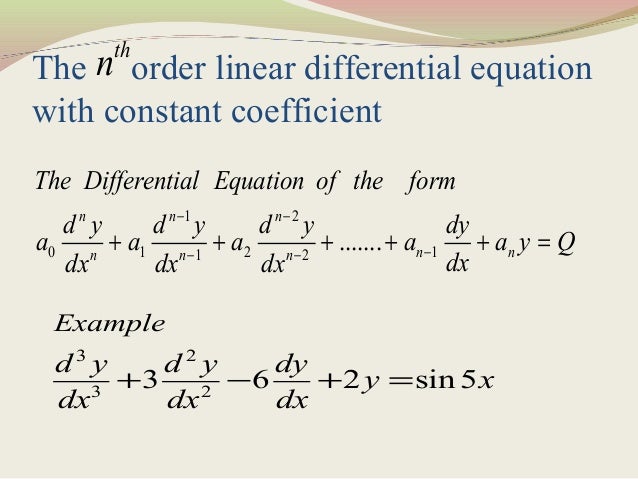
Linear Differential Equation With Constant Coefficient
Second Order Linear Nonhomogeneous Differential Equations With Variable Coefficients
Https Users Math Msu Edu Users Gnagy Teaching 12 Spring Mth235 L06 235 Pdf

Chapter 5 Partial Differential Equations Pdf
Ordinary Differential Equations

Chapter 6 Partial Differential Equations
Integration And Differential Equations
Integration And Differential Equations